Though heart rate variability (HRV) isn’t a new concept, its application in fitness devices, Sleep Number beds, and lifestyle trackers has made it a mainstream health and fitness measurement. But what is heart rate variability? How does your lifestyle affect it? Why is it such a valuable measurement to track over time?
In this ultimate guide, we’ll answer all those questions and many more. This guide is useful for health and fitness professionals and curious, everyday Joes and Janes. You can read from beginning to end, or use the shortcuts to jump to the most interesting topics.
- What is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
- The Importance of Heart Rate Variability for Health and Fitness
- How To Measure Heart Rate Variability
- Factors Affecting Heart Rate Variability
- The Connection Between Heart Rate Variability and Stress Levels
- Heart Rate Variability and Exercise Performance
- Heart Rate Variability and Recovery
- Heart Rate Variability Tracking Devices and Apps
- Interpreting HRV Data for Personal Health
What is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
When we talk about our bodies’ health and fitness, we often focus on visible aspects like muscle strength or endurance. However, a less visible but crucial indicator tells us a lot about our overall well-being: Heart Rate Variability (HRV).
This might sound like a complex scientific term, but understanding HRV is easier than you think, and it’s incredibly relevant to everyone, especially those in middle age striving for better health.
Heart rate variability refers to the variation in time between each heartbeat.
Contrary to what some might think, a healthy heart doesn’t beat with the regularity of a metronome. Instead, there are tiny variations in the time between heartbeats.
These variations are influenced by the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which regulates many of our body’s involuntary functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and digestion.1Shaffer, F., & Ginsberg, J. P. (2017). An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Frontiers in Public Health, 5, 258. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2017.00258
The autonomic nervous system has two main components: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems.
The sympathetic system is like your body’s accelerator; it’s responsible for the ‘fight or flight’ response, increasing heart rate and preparing your body for action. On the other hand, the parasympathetic system acts like a brake. It promotes ‘rest and digest’ responses, slowing down the heart rate and aiding in relaxation and recovery.
HRV identifies the balance between these two systems. It indicates good health and fitness when your body can rapidly switch between sympathetic and parasympathetic responses, adapting to different stressors and demands.2Thayer, J. F., Åhs, F., Fredrikson, M., Sollers, J. J., & Wager, T. D. (2012). A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: Implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(2), 747-756. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.11.009
High HRV is typically a sign of a healthy, resilient heart, while low HRV can be a warning sign of stress, fatigue, or underlying health issues.3Laborde, S., Mosley, E., & Thayer, J. F. (2017). Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Vagal Tone in Psychophysiological Research – Recommendations for Experiment Planning, Data Analysis, and Data Reporting. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 213. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00213
Understanding HRV gives us a window into the workings of our ANS and, by extension, our overall health. It’s a subtle but powerful way to listen to what’s happening inside our bodies. In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the importance of HRV, how it’s measured, and how we can use this knowledge to enhance our health and fitness.
The Importance of Heart Rate Variability for Health and Fitness
Heart rate variability is more than just a metric for cardiologists; it’s a critical health indicator for anyone interested in their fitness and well-being. HRV’s significance lies in its ability to offer real-time feedback about our body’s physiological state, making it an essential tool for both health enthusiasts and professionals.
1. Indicator of Autonomic Nervous System Health
HRV is an excellent gauge of the autonomic nervous system’s balance. A well-functioning ANS is crucial for overall health, as it regulates vital functions like heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. Studies have shown that a higher HRV is associated with better cardiovascular health, lower stress levels, and improved survival rates following a heart attack.4Thayer, J. F., Yamamoto, S. S., & Brosschot, J. F. (2010). The relationship of autonomic imbalance, heart rate variability and cardiovascular disease risk factors. International Journal of Cardiology, 141(2), 122-131. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2009.09.543
2. Stress and Recovery Marker
HRV is incredibly sensitive to changes in our body’s stress levels. It can differentiate between states of relaxation and high stress. For instance, during periods of high stress, HRV tends to decrease, reflecting the dominance of the sympathetic nervous system. Conversely, a relaxed state is marked by higher HRV, indicating parasympathetic dominance. This makes HRV an invaluable tool for monitoring stress and recovery, particularly in the context of mental health and well-being.5Kim, H. G., Cheon, E. J., Bai, D. S., Lee, Y. H., & Koo, B. H. (2018). Stress and Heart Rate Variability: A Meta-Analysis and Review of the Literature. Psychiatry Investigation, 15(3), 235-245. doi:10.30773/pi.2017.08.17
3. Predicting Exercise Performance and Recovery
In the realm of fitness, HRV has emerged as a key predictor of exercise performance and recovery. Athletes with higher HRV often experience better performance and faster recovery. It can also help in identifying the onset of overtraining syndrome, a common issue among athletes. By monitoring changes in HRV, trainers and athletes can adjust training loads to optimize performance while minimizing the risk of injury or burnout.6Bellenger, C. R., Fuller, J. T., Thomson, R. L., Davison, K., Robertson, E. Y., & Buckley, J. D. (2016). Monitoring Athletic Training Status Through Autonomic Heart Rate Regulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Medicine, 46(10), 1461-1486. doi:10.1007/s40279-016-0484-2
4. Personalized Health Insights
HRV offers personalized insights into one’s health. Each individual’s HRV is unique, and tracking changes over time can provide valuable information about personal health trends. This individualized data is particularly beneficial for tailoring fitness programs to one’s specific health needs, enhancing the effectiveness of exercise programs.7Plews, D. J., Laursen, P. B., Stanley, J., Kilding, A. E., & Buchheit, M. (2013). Training adaptation and heart rate variability in elite endurance athletes: Opening the door to effective monitoring. Sports Medicine, 43(9), 773-781. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0071-8
Understanding the importance of HRV in the context of health and fitness underscores its value as a powerful tool. It’s not just about the numbers; it’s about what those numbers tell us about our bodies. By paying attention to HRV, individuals can gain deeper insights into their health, leading to more informed decisions about stress management, exercise, and overall well-being.
How To Measure Heart Rate Variability
Understanding how to measure heart rate variability is crucial for effectively utilizing this insightful health metric. The process of measuring HRV might seem technical, but with advancements in technology, it has become more accessible than ever.
Electrocardiography (ECG/EKG)
Traditionally, HRV is measured using an Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This method, considered the gold standard, involves placing electrodes on the skin to record the heart’s electrical activity. By analyzing these recordings, medical professionals can calculate the time intervals between heartbeats, known as the RR intervals (the time between successive R-waves). This method provides the most accurate HRV readings and is widely used in clinical and research settings.8Shaffer, F., & Ginsberg, J. P. (2017). An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Frontiers in Public Health, 5, 258. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2017.00258
Photoplethysmography (PPG)
A more recent and increasingly popular method for measuring HRV is through Photoplethysmography (PPG). This technique utilizes light-based technology, often found in wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. PPG sensors measure the blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue, which are influenced by the heart’s pumping action. While PPG is less accurate than ECG, its convenience and non-invasive nature make it a popular choice for everyday HRV tracking.9Lu, S., Zhao, H., Ju, K., Shin, K., Lee, M., Shelley, K., & Chon, K. H. (2018). Can photoplethysmography variability serve as an alternative approach to obtain heart rate variability information? Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing, 32(1), 21-29. doi:10.1007/s10877-017-0008-7
Heart Rate Monitors
Specialized heart rate monitors, often used by athletes and fitness enthusiasts, also measure HRV. These devices typically use a chest strap sensor, which is more accurate than PPG sensors in fitness trackers but less invasive than an ECG. They provide a balance between accuracy and convenience, making them suitable for regular monitoring of HRV in relation to exercise and recovery.10Gil, E., Orini, M., Bailón, R., Vergara, J. M., Mainardi, L., & Laguna, P. (2015). Photoplethysmography Pulse Rate Variability as a Surrogate Measurement of Heart Rate Variability During Non-Stationary Conditions. Physiological Measurement, 31(9), 1271–1290. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/31/9/015
Smartphones and Mobile Apps
The proliferation of smartphones has led to the development of apps capable of measuring HRV. These apps often use the phone’s camera and flash to record PPG, similar to wearable devices. While they offer a high level of convenience, their accuracy can vary, and they should be used more for tracking trends rather than for precise measurements.11Plews, D. J., Laursen, P. B., Kilding, A. E., & Buchheit, M. (2017). Heart Rate Variability and Training Intensity Distribution in Elite Rowers. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 12(S2), S2-36–S2-43. doi:10.1123/ijspp.2016-0203
When measuring HRV, consistency is key. Whether using a clinical ECG, a wearable device, or a smartphone app, ensuring consistent measurement conditions – like the time of day and the body’s state (resting or active) – is crucial for obtaining reliable and comparable data.
Factors Affecting Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability is influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from physiological conditions to lifestyle choices. Understanding these factors is key to accurately interpreting HRV data and making informed health and fitness decisions.
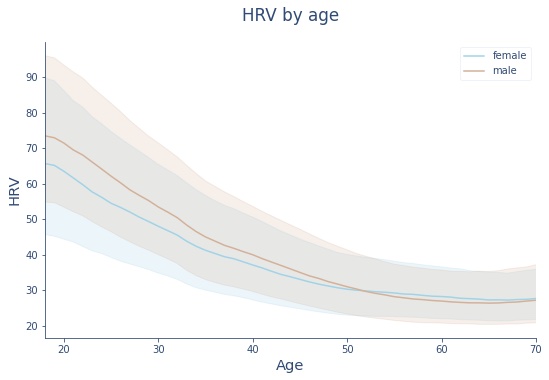
- Age and Gender: Age is a significant determinant of HRV. Generally, HRV decreases as people age, reflecting changes in the autonomic nervous system’s function over time. Gender also plays a role, with studies indicating that men and women may exhibit different HRV patterns due to varying hormonal influences.12Umetani, K., Singer, D. H., McCraty, R., & Atkinson, M. (1998). Twenty-four hour time domain heart rate variability and heart rate: Relations to age and gender over nine decades. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 31(3), 593-601. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00554-8
- Physical Fitness: A person’s level of physical fitness has a profound impact on HRV. Regular physical activity, particularly aerobic exercise, is known to enhance HRV, indicating a more resilient and adaptable heart. Athletes and physically active individuals often show higher HRV compared to their less active counterparts.13Stanley, J., Peake, J. M., & Buchheit, M. (2013). Cardiac Parasympathetic Reactivation Following Exercise: Implications for Training Prescription. Sports Medicine, 43(12), 1259-1277. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0083-4
- Stress and Emotional State: Mental stress and emotional states like anxiety can significantly reduce HRV. The body’s stress response, mediated by the sympathetic nervous system, can lead to a decrease in HRV, indicating a state of heightened stress or reduced resilience to stress.14Thayer, J. F., Yamamoto, S. S., & Brosschot, J. F. (2012). The relationship of autonomic imbalance, heart rate variability and cardiovascular disease risk factors. International Journal of Cardiology, 141(2), 122-131. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2009.09.543
- Sleep Quality: Sleep plays a vital role in regulating HRV. Poor sleep quality or irregular sleep patterns can lead to lower HRV. Conversely, good sleep hygiene is associated with higher HRV, reflecting better cardiovascular health and stress resilience.15Tobaldini, E., Cogliati, C., Fiorelli, E. M., Nunziata, V., Wu, M. A., Prado, M., … & Montano, N. (2013). One night on-call: Sleep deprivation affects cardiac autonomic control and inflammation in physicians. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 24(7), 664-670. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2013.03.011
- Nutrition: Nutritional choices profoundly affect HRV. Diets high in processed foods and sugars can adversely impact HRV, while a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is associated with higher HRV. Nutrition plays a critical role in managing inflammation and oxidative stress, which in turn influences heart health and HRV.16Koenig, J., & Thayer, J. F. (2016). Sex differences in healthy human heart rate variability: A meta-analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 64, 288-310. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.007
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol has a complex relationship with HRV. Moderate alcohol consumption might have a beneficial effect on HRV, but excessive drinking is detrimental. Heavy alcohol use is associated with a significant reduction in HRV, indicating impaired autonomic function (Thayer et al., 2006).
- Lifestyle Choices: Factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor dietary habits can negatively affect HRV. These lifestyle choices can lead to a decrease in HRV, reflecting their adverse effects on heart health and overall well-being.17Thayer, J. F., Hall, M., Sollers, J. J., & Fischer, J. E. (2006). Alcohol use, urinary cortisol, and heart rate variability in apparently healthy men: Evidence for impaired inhibitory control of the HPA axis in heavy drinkers. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 59(3), 244-250. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2005.10.013
- Medical Conditions: Various medical conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes, can influence HRV. These conditions often result in lower HRV, highlighting the importance of HRV as an indicator of health status.18Kleiger, R. E., Miller, J. P., Bigger Jr, J. T., & Moss, A. J. (1987). Decreased heart rate variability and its association with increased mortality after acute myocardial infarction. The American Journal of Cardiology, 59(4), 256-262. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(87)90795-8
- Supplements: The use of certain dietary supplements can influence HRV. For instance, omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil, have been shown to improve HRV, suggesting a protective effect on heart health. Similarly, supplements that aid in stress reduction, such as magnesium or adaptogenic herbs, may also positively impact HRV. However, the effects of supplements can vary widely among individuals, and it’s important to choose supplements based on personal health needs and under professional guidance.19Hansen, A. L., Harris, W. S., & Mostofsky, E. (2017). Fish consumption, omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease. The Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing, 32(6), 538-545. doi:10.1097/JCN.0000000000000421
By considering these factors, individuals and fitness professionals can better understand HRV readings and how they relate to overall health and well-being. This understanding is crucial for designing personalized health and fitness programs that cater to individual needs and conditions.
The Connection Between Heart Rate Variability and Stress Levels
The link between heart rate variability (HRV) and stress levels is a critical aspect of understanding how our bodies respond to various stressors, both psychological and physical. This connection is rooted in the intricate workings of our autonomic nervous system (ANS) and its response to stress.
The Autonomic Nervous System and Stress
The ANS, which includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, plays a pivotal role in our body’s stress response.
Under stress, the sympathetic nervous system kicks into high gear, triggering the ‘fight or flight’ response. This reaction decreases HRV, as the heart rate becomes more consistent and less variable to prepare for immediate action.
Conversely, during periods of relaxation, the parasympathetic nervous system dominates, increasing HRV and promoting a state of calm and recovery.
HRV as a Stress Indicator
HRV serves as a non-invasive, real-time indicator of stress levels.
A lower HRV is often associated with higher stress levels, indicating that the body is in a heightened state of sympathetic activation. Conversely, higher HRV suggests a relaxed state with dominant parasympathetic activity.
This makes HRV a valuable tool for monitoring stress and assessing an individual’s capacity to handle stress.
Psychological Stress and HRV
Psychological stress, such as anxiety or chronic stress, can have a pronounced effect on HRV.
Chronic psychological stress is linked to a consistently lower HRV, suggesting a prolonged sympathetic dominance and reduced resilience to stress. This relationship has made HRV a focus in mental health research, providing insights into how stress impacts our overall health.20Hall, M., Vasko, R., Buysse, D., Ombao, H., Chen, Q., Cashmere, J. D., … & Thayer, J. F. (2004). Acute stress affects heart rate variability during sleep. Psychosomatic Medicine, 66(1), 56-62. doi:10.1097/01.psy.0000106884.58744.f9
Physical Stress and HRV
Physical stressors, like intense exercise or physical exertion, also influence HRV.
During physical activity, HRV decreases as the heart rate rises to meet the body’s increased demand for blood and oxygen. Post-exercise, HRV can provide valuable information about recovery status and readiness for further physical activity.21Stanley, J., Peake, J. M., & Buchheit, M. (2013). Cardiac Parasympathetic Reactivation Following Exercise: Implications for Training Prescription. Sports Medicine, 43(12), 1259-1277. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0083-4
Stress Management and HRV Improvement
Understanding the connection between HRV and stress levels opens the door to effective stress management strategies. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, and yoga have been shown to improve HRV by enhancing parasympathetic activity and reducing stress.22Lehrer, P. M., & Gevirtz, R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 756. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
The interplay between HRV and stress levels is a testament to the body’s remarkable adaptability. By monitoring and understanding HRV, individuals can gain insights into their stress levels, guiding them toward healthier lifestyle choices and stress management techniques.
Heart Rate Variability and Exercise Performance
The relationship between heart rate variability and exercise performance is a fascinating and crucial area, especially for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Understanding this relationship can significantly enhance training effectiveness and optimize athletic performance.
HRV as a Predictor of Exercise Capacity
HRV is increasingly recognized as a valuable predictor of exercise performance. Athletes with higher HRV typically exhibit better physical performance, endurance, and readiness for training. This is because a higher HRV often signifies a well-balanced autonomic nervous system, which is essential for optimal physical performance.23Bellenger, C. R., Fuller, J. T., Thomson, R. L., Davison, K., Robertson, E. Y., & Buckley, J. D. (2016). Monitoring Athletic Training Status Through Autonomic Heart Rate Regulation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Medicine, 46(10), 1461-1486. doi:10.1007/s40279-016-0484-2
Training Intensity and HRV
The intensity of exercise has a direct impact on HRV. During intense training or exercise, HRV decreases as the heart rate increases to meet the body’s heightened demand for oxygen and nutrients. Monitoring HRV in relation to training intensity helps in identifying the body’s response to different training loads, allowing for adjustments to maximize performance and avoid overtraining.24Plews, D. J., Laursen, P. B., Stanley, J., Kilding, A. E., & Buchheit, M. (2013). Training adaptation and heart rate variability in elite endurance athletes: Opening the door to effective monitoring. Sports Medicine, 43(9), 773-781. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0071-8
Overtraining Syndrome and HRV
Overtraining syndrome, a condition of prolonged fatigue and performance decline due to excessive training, is closely associated with changes in HRV. Athletes experiencing overtraining syndrome often show a sustained reduction in HRV, indicating an imbalance in autonomic nervous system activity. Regular HRV monitoring can help in early detection of overtraining, enabling timely intervention and recovery strategies.25Stanley, J., Peake, J. M., & Buchheit, M. (2013). Cardiac Parasympathetic Reactivation Following Exercise: Implications for Training Prescription. Sports Medicine, 43(12), 1259-1277. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0083-4
Recovery and HRV
Post-exercise recovery is a crucial component of athletic training, and HRV plays a key role in this process. After physical exertion, HRV can provide valuable insights into the body’s recovery status. A return to baseline HRV levels indicates adequate recovery, whereas prolonged alterations may suggest insufficient recovery or potential overtraining.
Personalized Training Based on HRV
Utilizing HRV data can lead to more personalized training programs. By monitoring HRV responses to different training stimuli, fitness professionals can tailor training regimens to individual athletes’ recovery needs and physiological responses, thereby optimizing performance and reducing the risk of injury.
The connection between HRV and exercise performance is a powerful tool in the arsenal of athletes and fitness professionals. It offers a deeper understanding of the body’s responses to training, guiding more informed decisions in exercise programming and recovery management.
Heart Rate Variability and Recovery
The role of heart rate variability in the recovery process is vital to fitness and overall health. HRV helps assess the state of recovery and optimize recovery strategies for better health and performance.
HRV as a Recovery Indicator
Post-exercise, HRV serves as an important indicator of the body’s recovery status. Following physical exertion, the body enters a recovery phase, where the parasympathetic nervous system aids in restoring balance. An increase in HRV during this period is a positive sign, indicating effective recovery and a well-functioning autonomic nervous system.26Stanley, J., Peake, J. M., & Buchheit, M. (2013). Cardiac Parasympathetic Reactivation Following Exercise: Implications for Training Prescription. Sports Medicine, 43(12), 1259-1277. doi:10.1007/s40279-013-0083-4
Understanding Recovery Needs
Individual responses to exercise vary greatly, and so do recovery needs. HRV can provide personalized insights into these recovery needs. By monitoring HRV, individuals and trainers can gauge whether the body is adequately recovered or if more rest is needed before the next training session.
Managing Training Loads
HRV monitoring helps in managing training loads effectively. If HRV remains suppressed following a training session, it may suggest that the athlete is still recovering and that further intense training could lead to overtraining or injury. Adjusting training loads based on HRV readings can prevent these adverse outcomes and enhance overall performance.
Recovery Techniques and HRV
Different recovery techniques, such as active recovery, sleep, nutrition, and stress management, can influence HRV. For example, techniques that enhance parasympathetic activity, like deep breathing exercises or yoga, can be beneficial in improving HRV during recovery phases.27Lehrer, P. M., & Gevirtz, R. (2014). Heart rate variability biofeedback: How and why does it work? Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 756. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00756
Long-term Health Implications
Beyond athletic performance, HRV during recovery periods has broader health implications. Consistently low HRV during recovery can be a sign of inadequate stress management or potential health issues, emphasizing the importance of balanced training and recovery practices for long-term health.
In essence, HRV is a powerful tool in the recovery toolkit. Whether for an athlete optimizing performance or an individual focused on general health, understanding and applying HRV data can lead to more effective recovery strategies and better overall health outcomes.
Using HRV to Optimize Training and Prevent Overtraining
Incorporating heart rate variability into training regimes offers a sophisticated approach to optimizing workout effectiveness and preventing the pitfalls of overtraining. By understanding and applying HRV data, individuals can tailor their exercise routines for maximum benefit while safeguarding their health.
Tailoring Training Intensity
HRV is instrumental in determining the body’s readiness for exercise. On days when HRV is higher than an individual’s baseline, it may indicate a readiness for more intense training. Conversely, a lower HRV suggests the need for lighter activity or rest. This approach ensures that training intensity aligns with the body’s current stress and recovery status, enhancing training effectiveness.28Buchheit, M. (2014). Monitoring training status with HRV measures: Do all roads lead to Rome? Frontiers in Physiology, 5, 73. doi:10.3389/fphys.2014.00073
Monitoring Overtraining Risks
Consistent tracking of HRV can serve as an early warning system for overtraining. A significant or sustained decrease in HRV can be a signal that the body is not recovering adequately, indicating a risk of overtraining. This information is crucial for adjusting training plans, allowing for adequate rest and recovery, thereby preventing overtraining syndrome, which is characterized by fatigue, decreased performance, and potential health risks.29Saw, A. E., Main, L. C., & Gastin, P. B. (2016). Monitoring the athlete training response: Subjective self-reported measures trump commonly used objective measures: a systematic review. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 50(5), 281-291. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2015-094758
Periodization and Peaking
In the context of periodized training, HRV can guide the timing of high-intensity and low-intensity phases. By planning training loads in harmony with HRV trends, athletes can peak at the right time for competitions, ensuring they are in optimal condition when it matters most.
Long-term Health and Performance
Using HRV as a guide, individuals can strike a balance between training and recovery, which is essential for long-term health and sustained performance. This balanced approach not only enhances athletic longevity but also contributes to overall well-being.
HRV offers a window into the body’s recovery state and stress levels, providing invaluable guidance for personalizing training schedules. By respecting the body’s signals, as indicated by HRV, athletes and fitness enthusiasts can achieve their goals more effectively and sustainably.
Heart Rate Variability Tracking Devices and Apps
In today’s tech-driven world, monitoring heart rate variability has become more accessible than ever, thanks to a variety of devices and applications designed for this purpose. Understanding the options available and how to use them effectively can enhance one’s approach to health and fitness.
Types of HRV Tracking Tools
The market offers a range of devices and apps for HRV tracking. Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches commonly feature HRV monitoring capabilities. These devices use photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors to measure heart rate and HRV. Additionally, chest strap monitors, which may offer more accuracy, are popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. For those who prefer simplicity, smartphone apps utilizing the camera and flash to measure HRV can be a convenient option, though they may vary in accuracy.30Plews, D. J., Laursen, P. B., Kilding, A. E., & Buchheit, M. (2017). Heart Rate Variability and Training Intensity Distribution in Elite Rowers. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 12(S2), S2-36–S2-43. doi:10.1123/ijspp.2016-0203
Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the right HRV tracking tool depends on individual needs and preferences. For everyday fitness enthusiasts, a smartwatch or fitness tracker that offers HRV data along with other health metrics might be sufficient. Athletes and those seeking more precise data might opt for a chest strap monitor. It’s important to consider factors like ease of use, accuracy, and additional features when choosing a device or app.
Consistency in Measurement
Regardless of the chosen tool, consistency in measurement is key for accurate HRV tracking. It should ideally be measured at the same time each day, under similar conditions, to ensure reliable data. For instance, many people find that taking measurements first thing in the morning, after waking up, provides the most consistent results.
Interpreting the Data
While these tools provide valuable data, interpreting HRV readings correctly is crucial. Many devices and apps offer guidelines and interpretations of HRV scores, but understanding the context—such as current stress levels, recent physical activity, and overall health—is essential for accurate interpretation.
Incorporating HRV tracking into one’s routine can offer profound insights into health and fitness. By selecting the appropriate tool and using it consistently and intelligently, individuals can make more informed decisions about their training, recovery, and overall well-being.
Interpreting HRV Data for Personal Health
Effectively interpreting heart rate variability data is key to unlocking its potential for personal health insights. HRV is not just a number; it’s a reflection of the body’s complex physiological state and can be influenced by a variety of factors.
- Understanding Baseline HRV: The first step in interpreting HRV data is to establish a personal baseline. This baseline is unique to each individual and can be determined by consistently tracking HRV over a period of time. Fluctuations from this baseline can provide insights into changes in stress levels, recovery status, and overall health.
- Contextualizing HRV Readings: It’s crucial to interpret HRV data within the context of one’s overall lifestyle and health. Factors such as sleep quality, physical activity, stress, nutrition, and even time of day can influence readings. For example, a lower HRV reading following a poor night’s sleep or a high-stress day might not be unusual and should be interpreted differently than a similar reading under restful conditions.
- Tracking HRV Trends Over Time: Instead of focusing on day-to-day variations, paying attention to longer-term trends in HRV can be more informative. Significant changes over weeks or months can indicate changes in health status or the effectiveness of lifestyle interventions. For instance, a gradual increase in HRV over time might suggest improvements in fitness levels or stress management.
- Seeking Professional Guidance: While HRV tracking devices and apps provide valuable data, they are not substitutes for professional medical advice. Significant or persistent changes in HRV, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, should prompt consultation with a healthcare provider.
- Integrating HRV with Other Health Metrics: To get the most comprehensive view of one’s health, HRV data should be considered alongside other health indicators such as blood pressure, heart rate, and fitness levels. This holistic approach can help in making more informed decisions about health and wellness strategies.
In summary, HRV is a powerful tool for personal health monitoring, offering insights that can guide lifestyle choices and health interventions. However, its interpretation requires a nuanced understanding of individual health contexts and should ideally be part of a broader health assessment.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Heart Rate Variability for Better Health and Fitness
Heart rate variability is much more than a mere health metric; it is a gateway to understanding our body’s inner workings and its response to stress, recovery, and overall well-being. The journey through the various facets of HRV reveals its profound impact on health and fitness, offering insights that can guide us towards a more balanced and healthier lifestyle.
A Tool for Empowerment: HRV empowers individuals by providing real-time feedback on their physiological state. Whether it’s adjusting training intensity, monitoring stress and recovery, or making informed lifestyle choices, HRV serves as a personal health compass. It encourages a proactive approach to health, where decisions are data-driven and tailored to individual needs.
Personalization of Health Strategies: The beauty of HRV lies in its individuality. Each person’s HRV is unique, and tracking it over time offers personalized insights. This personalization is key in crafting health and fitness strategies that are not only effective but also sustainable in the long run.
Beyond Fitness: While HRV is particularly valuable for athletes and fitness enthusiasts, its benefits extend to anyone interested in improving their health. By linking physiological responses to lifestyle factors such as sleep, nutrition, and stress management, HRV provides a holistic view of one’s health.
The Future of Health Monitoring: As technology advances, the ease of monitoring HRV will continue to grow, making it an increasingly integral part of personal health management. This accessibility presents a tremendous opportunity for widespread education and utilization of HRV in everyday health practices.
In essence, HRV is a powerful ally in our quest for better health and fitness. By understanding and utilizing this tool, we can unlock a deeper awareness of our bodies, leading to more informed health decisions, optimized fitness plans, and a greater sense of control over our overall well-being.



